
“Among several commercial services who have claimed to be specialized to generate mouse models with genetic modifications, I recognize that Cyagen is one of the best. We are looking forward to having more cooperation with them.”
Korea Brain Research Institute (KBRI)We will respond to you in 1-2 business days.
The syngeneic model (also known as allograft mouse tumor systems) involves inoculation of tumor cell lines (derived from the same genetic background strain) which are implanted into the inbred immunocompetent mouse strain. The recipient mouse has an intact native immune system and normal immune response, and its immune system is compatible with the transplanted tumor tissue - which together maximize the simulation of the real-life tumor microenvironment. However, the transplanted mouse tissue may not fully represent the complexity of human tumors in clinical cases.
Cyagen can provide various pharmacological evaluation methods, such as tumor growth curve/weight curve, blood biochemical indicators, pathological test (frozen section and paraffin section examination, H&E staining, immunohistochemistry (IHC), etc.), flow cytometry, molecular testing, which can meet your multiple needs for the analysis of drug mechanism.
Backgrounds: Generally C57BL/6 or BALB/c
Injection Site:
● Subcutaneous: Convenient to directly observe tumor growth
● In situ: Simulate the original environment of tumor growth
● System injection: Intraperitoneal or intravenous injection to monitor the tumor spreading, or metastasis
Cyagen can provide you with various syngeneic models, such as breast cancer, liver cancer, colon cancer, melanoma, lung cancer, and brain cancer models, as well as highly customized in vivo pharmacodynamic services for the corresponding models.
Selected Syngeneic Model Cases
CT26.WT murine colon carcinoma subcutaneous tumor model
Figure 1. The growth curve of CT26.WT murine colon carcinoma subcutaneous tumor
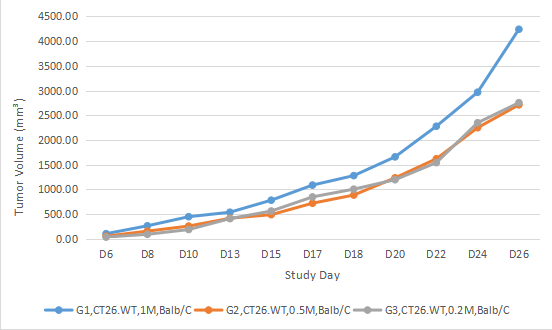
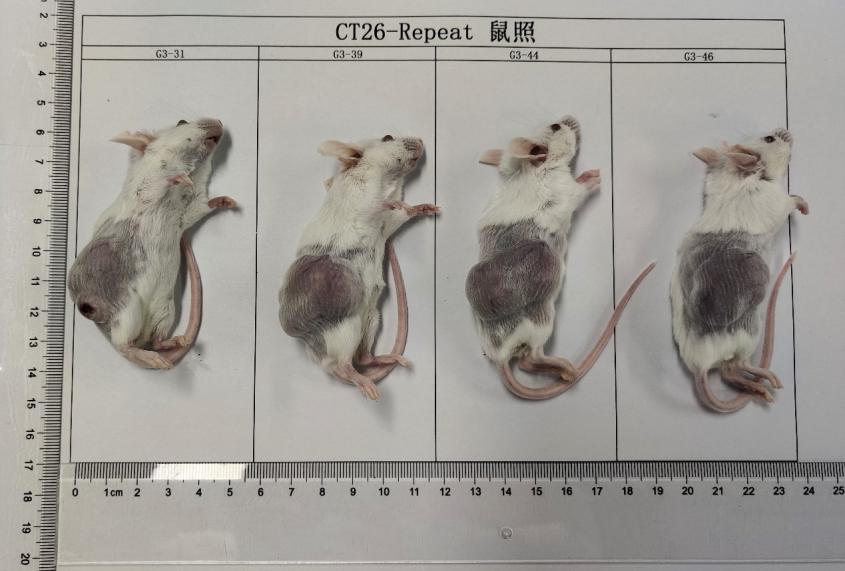
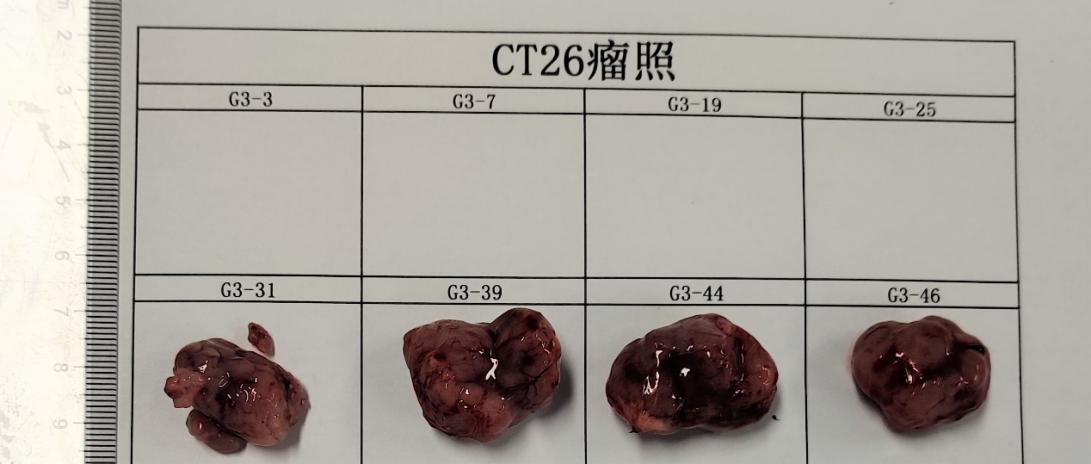
Figure 2. Formation experiment of CT26.WT cell subcutaneous tumor. CT26.WT cells were inoculated into BALB/c mice through subcutaneous injection, to explore the tumor volume of different concentrations of cell inoculation.